Roe v Wade and state abortion policies: By the numbers | Women’s Rights News
Several US states have abortion bans and restrictions that could go into effect if the landmark 1973 ruling is reversed.
A leaked United States Supreme Court draft majority opinion that would strike down the 1973 Roe v Wade ruling, which made abortion legal nationwide, has raised the prospect of abortions again becoming illegal across swathes of the country.
Overturning the 1973 ruling, which conservative Supreme Court Justice Samuel Alito called in the leaked draft opinion “egregiously wrong from the start”, would again leave final decisions on abortion access to state governments, barring the passage of federal legislation.
Officials in several states have for years prepared for a scenario where access to abortion is no longer considered a constitutional right, passing legislation to ban abortions. In several cases the bans could immediately go into effect in the event Roe v Wade is struck down.
At least six states – including Alabama, Arizona, Michigan, North Carolina, West Virginia, and Wisconsin – have retained their pre-1973 bans on abortions, although they are unenforced.
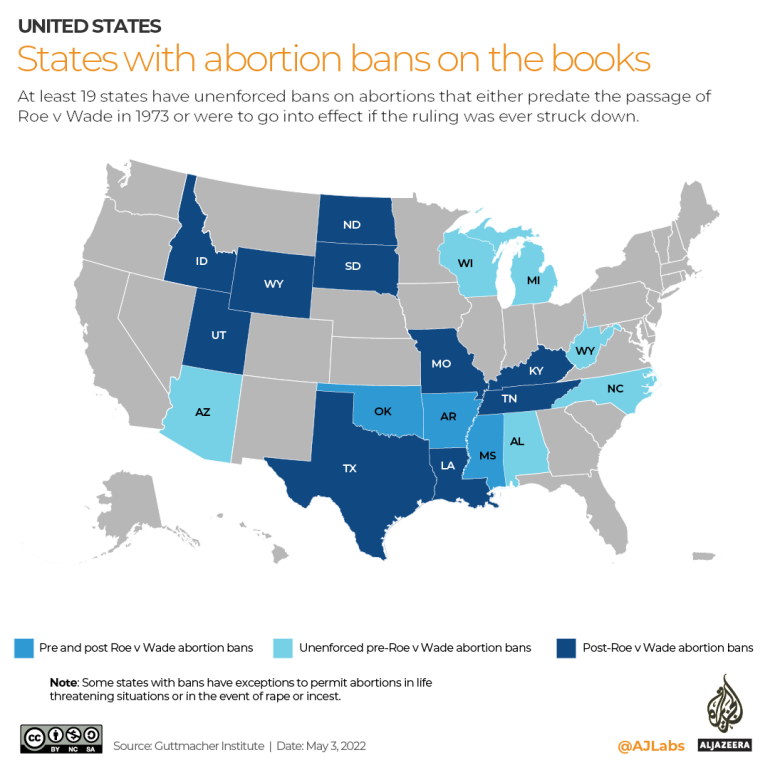
Ten states – Idaho, Kentucky, Louisiana, Missouri, North Dakota, South Dakota, Tennessee, Texas, Utah, and Wyoming – have passed laws “to ban all or nearly all abortions that would be triggered if Roe were overturned”, according to the Guttmacher Institute.
Three states – Arkansas, Mississippi, and Oklahoma – have both pre- and post-1973 bans on the books.
Some, but not all, of the states that have pending bans on abortions would permit the procedure if the life or health of the mother is at risk or in cases of rape.
Meanwhile, at least nine states have restrictions on access to abortion that could go into effect if Roe v Wade is struck down.
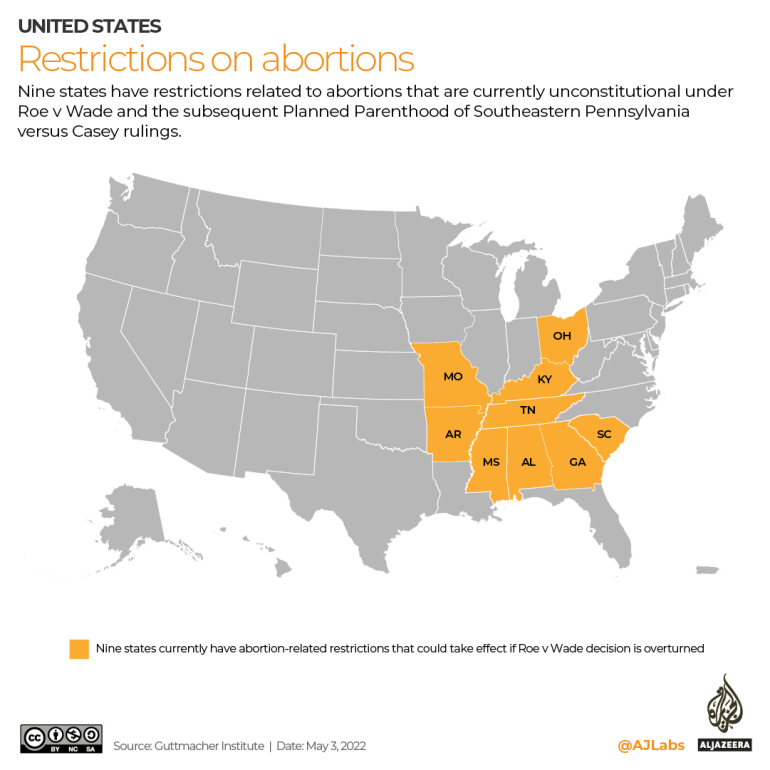
While the restrictions do not amount to an overall ban, they include bans on abortions after a heartbeat can be detected, typically within the first six weeks of pregnancy before most women know they’re pregnant.
Other restrictions include requirements that doctors in the state have admitting privileges to perform an abortion.
That provision was previously deemed unconstitutional based on the 1992 Supreme Court ruling in the Planned Parenthood of Southeastern Pennsylvania v Casey case, which prohibited measures that put “undue burdens” on individuals seeking abortions.

On the flip side of the issue, several states in recent years have passed legislation to protect the right to access to abortion.
Four states and the District of Colombia protect the right to abortion throughout the entire pregnancy.
Twelve other states – California, Connecticut, Delaware, Hawaii, Illinois, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, Nevada, New York, Rhode Island, and Washington – have passed laws to protect the right to abortion prior to viability, typically defined as the point when a doctor determines the fetus could reasonably survive outside of the womb.





Pingback: 티비위키
Pingback: KIU
Pingback: true albino teacher mushroom potency
Pingback: ติดตั้ง ais fiber