Yemen’s war explained in maps and charts | Infographic News
Yemen is facing one of the world’s worst humanitarian crises as the brutal war there enters its eighth year.
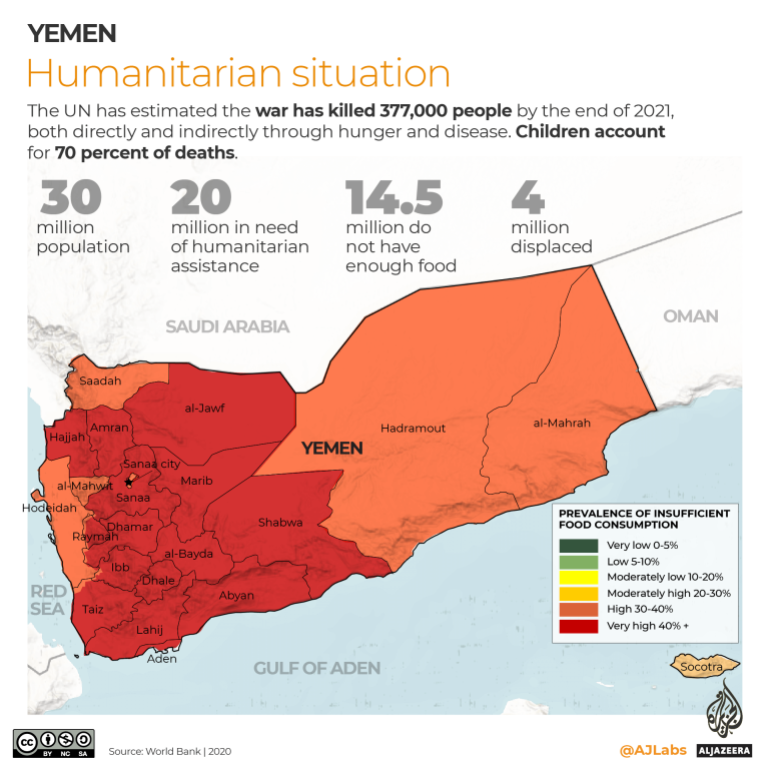
The UN estimates the war has killed 377,000 people as of the end of 2021, both directly and indirectly through hunger and disease – 70 percent of those deaths are children.
Nearly half the country (14.5 million) of 30 million people do not have enough food, according to the World Food Programme.
Nearly half (47.5 percent) of the children under five face chronic malnutrition.
At least 4 million people displaced have been displaced by the seven years of war.
Key players in the conflict
In March 2015, a Saudi-led coalition – backed by the United States – intervened militarily in Yemen in a bid to fight the Iran-backed Houthi rebels, restore President Abd-Rabbu Mansour Hadi’s government, and reverse what they say is growing Iranian influence in the region.
The Houthi armed group made international headlines after seizing control of Saada province in early 2014. They later moved southwards to seize the capital Sanaa and demanded constitutional change and power-sharing with the government. This forced Yemen’s Hadi to flee his presidential palace in Aden for Saudi Arabia.
Amid the instability, several other armed groups emerged, including al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula (AQAP), the UAE-backed separatist Southern Transitional Council (STC), and others.
The Houthis – also known as Ansar Allah – are a movement of mostly Zaidi Shia Muslims from Northern Yemen who opposed Hadi’s government and are believed to be supported by Iran.
Years of UN-brokered peace talks have failed to break the deadlock.

Who controls what in Yemen?
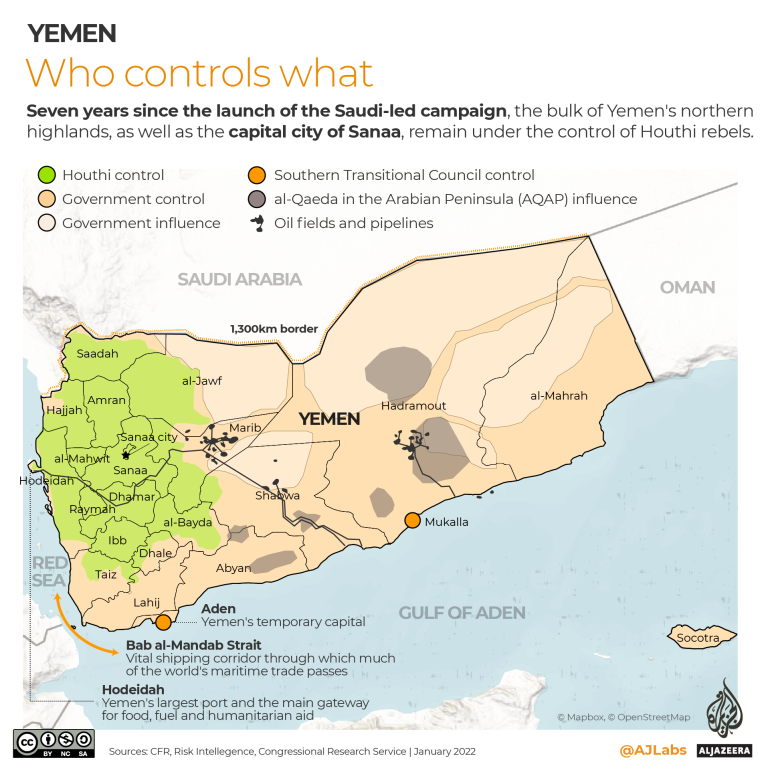
Seven years since the launch of the Saudi-led campaign, the bulk of Yemen’s northern highlands, as well as Sanaa, remain under the control of Houthi rebels.
The mountainous country between the Horn of Africa and the Middle East shares a 1,300km (800-mile) border with Saudi Arabia. Along its west coast is the Bab el-Mandeb Strait (“Gate of Tears” in Arabic), a vital shipping corridor through which much of the world’s maritime trade passes.
In the south is the port city of Aden, which was captured by the STC in 2019. Aden is the temporary home of Yemen’s internationally recognised government.
Air raids on Yemen
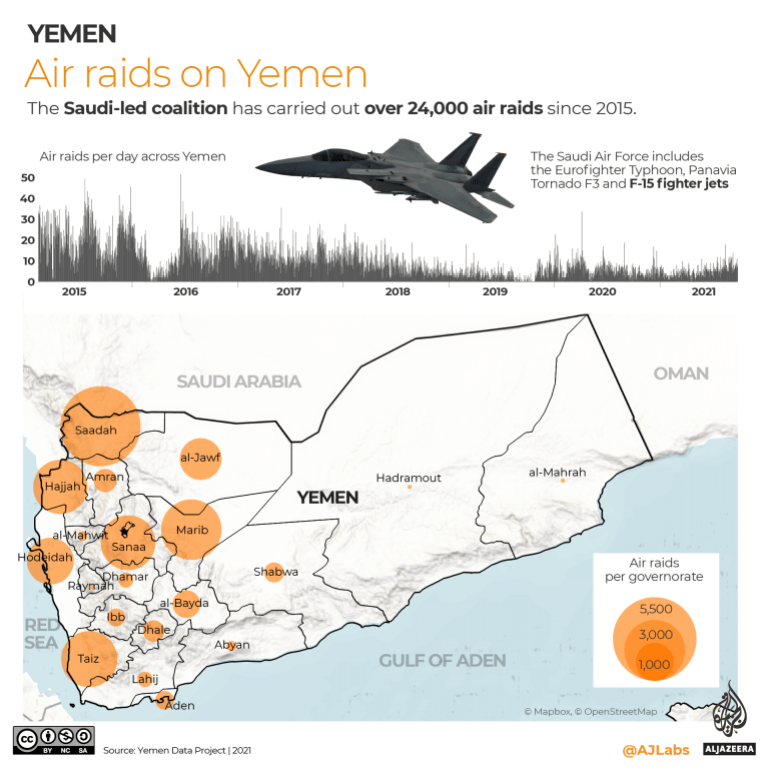
The Saudi-led coalition has carried out more than 24,000 air raids since 2015, according to data collected by the Yemen Data Project. Nearly two-thirds of these raids have struck non-military or unknown targets.
When the aerial campaign commenced on March 26, 2015, expectations were high that the coalition assembled by Saudi Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman would defeat the alliance of Houthi rebels and army forces loyal to late President Ali Abdullah Saleh within weeks.
Since 2015, human rights group Amnesty International has investigated dozens of air attacks across Yemen and found many instances where civilians were killed with US-made bombs.
Attacks on Saudi Arabia and the UAE
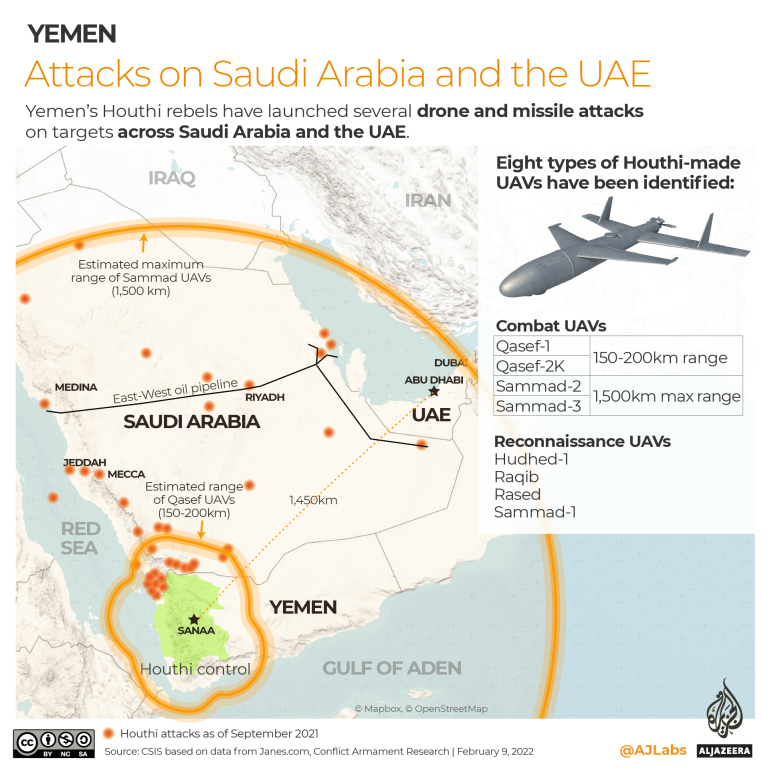
Over the years, Houthi rebels have targeted strategic infrastructure across Saudi Arabia and the UAE, including airports, gas fields and oil tankers in the Red Sea.
In recent weeks, tensions escalated as the Houthis started launching drone and missile attacks on the UAE – a member of a Saudi-led coalition.
According to a data analysis by the Center for Strategic and International Studies (CSIS), Saudi Arabia’s military has intercepted more than 4,000 Houthi missiles, drones and other standoff weapons over the past five years.
In response, the coalition has stepped up attacks in Saada province, northern Yemen and the Houthi-controlled capital, Sanaa.
According to the Conflict Armament Research group, eight types of Houthi-made drones, or unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), have been identified:
Combat UAVs: Qasef-1, Qasef-2K, Sammad-2, Sammad-3
The Qasef drones are estimated to have a range of 150-200km (93-124 miles) while the more advanced Sammads have an estimated maximum range of 1,500km (932 miles) – enough to reach the UAE from Houthi-controlled areas of Yemen.
Reconnaissance UAVs: Hudhed-1, Raqib, Rased and Sammad-1
On February 2, a little-known armed group in Iraq calling themselves Alwiyat al-Waad al-Haq (AWH), or the True Promise Brigades, claimed to have launched an attack on Abu Dhabi – suggesting the UAE is now being targeted from north and south.
Following the attacks, the US confirmed that it will bolster the UAE’s defences and send a guided-missile warship and advanced fifth-generation fighter jets there. The UAE hosts about 2,000 US troops, who provide early-warning intelligence and collaborate on air defence.
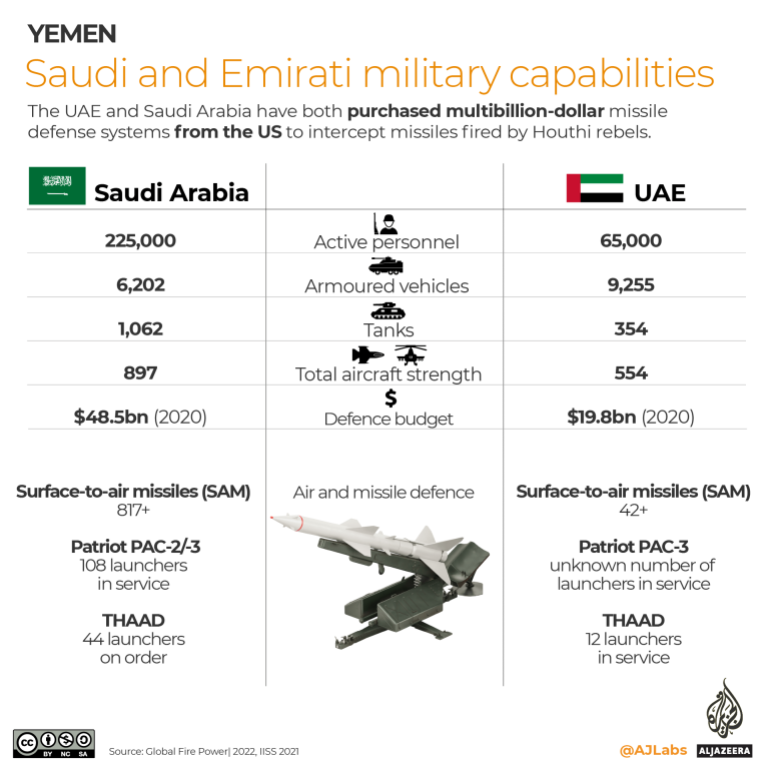
Saudi and Emirati military capabilities
Saudi Arabia and the UAE have both purchased multibillion-dollar missile defence systems from the US.
On January 17, US Central Command chief General Kenneth “Frank” McKenzie confirmed that the THAAD (Terminal High Altitude Area Defense) was used in combat for the first time against Houthi missiles fired towards the UAE.
The US military has had a presence in the Gulf for decades and has thousands of troops as well as a sizeable navy presence across the region.
Saudi Arabia’s military spending
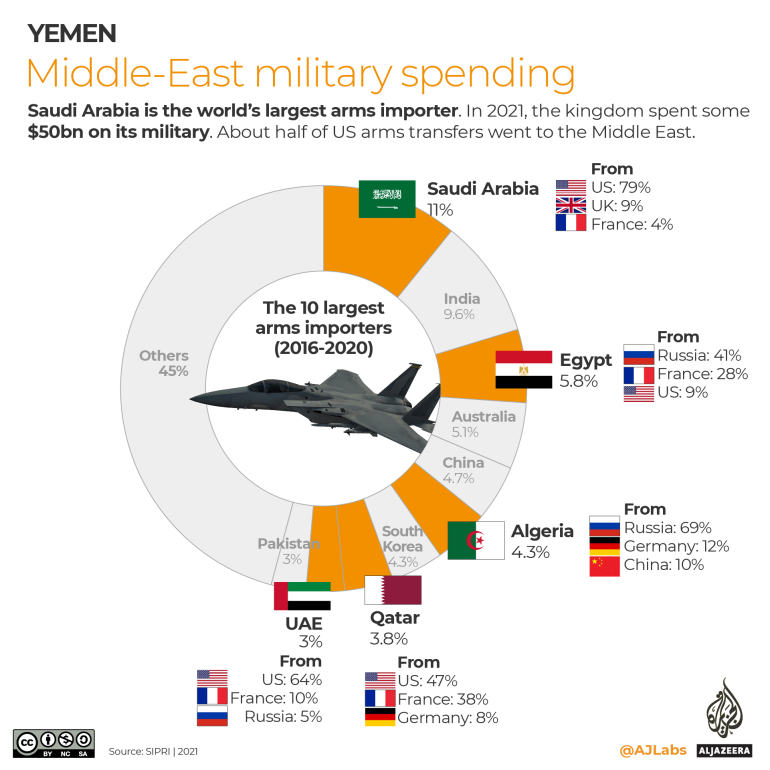
Saudi Arabia is the world’s largest arms importer. In 2020, the oil-rich kingdom spent $57.5bn – 8.4 percent of its GDP – on its military, according to the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI) (pdf).
In 2021, the kingdom said it spent some $50bn on its armed forces and is planning to spend about $46bn in 2022.
The US provides Saudi Arabia with 79 percent of its weapons, followed by the UK, with 9 percent and 4 percent from France (pdf). Saudi Arabia is also the main buyer of US, UK and Canadian weapons.
Between 2016 and 2020, nearly a quarter (24 percent) of the US’s, 32 percent of the UK’s and 49 percent of Canada’s total arms exports were to Saudi Arabia.
According to SIPRI, about half (47 percent) of US arms transfers over the past 5 years were to the Middle East.





Pingback: cele mai bune medicamente pentru articulatii